What is hantavirus, the cause of Gene Hackman’s wife’s death?
Legendary actor Gene Hackman, 95, and his wife, Betsy Arakawa Hackman, 65, have passed away, with their causes of death now confirmed by New Mexico authorities.
According to reports, Hackman succumbed to atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease and advanced Alzheimer’s disease, while his wife likely passed away first due to hantavirus pulmonary syndrome (HPS)—a rare but serious respiratory disease.
What Is Hantavirus Pulmonary Syndrome?
HPS is caused by hantaviruses, a group of viruses primarily carried by rodents. Dr. Rhys Parry, a molecular virologist at the University of Queensland, explains that these viruses can lead to severe respiratory and renal conditions in humans.
👉 Gene Hackman Death Timeline: A Look at His Final Days with Wife
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), hantaviruses found in North, Central, and South America are known to cause HPS. However, the CDC clarifies that hantaviruses in the U.S. are not known to spread from person to person.
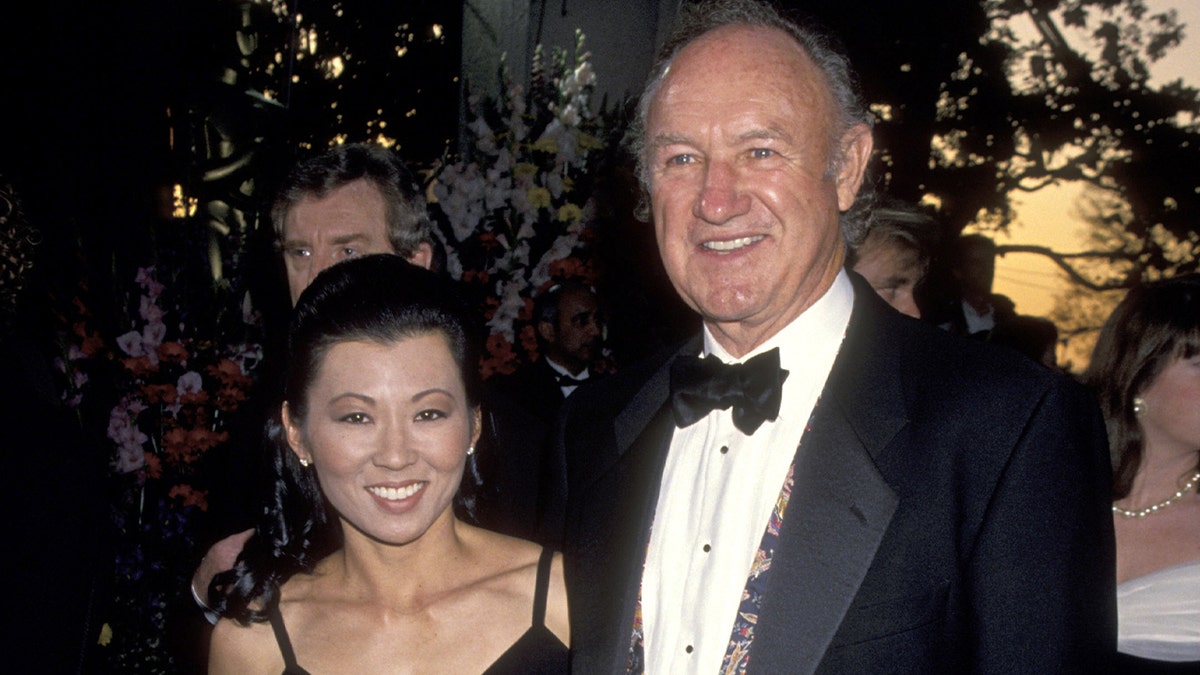

Causes of death have been revealed for actor Gene Hackman, 95, and his wife Betsy Arakawa Hackman, 65. (Getty Images)
Hantavirus Pulmonary Syndrome: A Deadly Disease with a 40% Fatality Rate
According to health experts, Hantavirus Pulmonary Syndrome (HPS) carries a nearly 40% fatality rate for those infected, making it a serious public health concern.
How Does Hantavirus Spread?
Dr. Rhys Parry, a molecular virologist, explains that hantaviruses primarily spread when humans inhale virus particles from rodent urine, droppings, or nesting materials.
👉 Deadly Virus Samples Go Missing in Major Biosecurity Breach – Authorities Investigate
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) lists several ways hantavirus can spread:
✔ Inhaling contaminated air while cleaning areas where rodents have been present
✔ Touching contaminated objects and then touching the face (nose or mouth)
✔ Bites or scratches from an infected rodent
✔ Consuming food contaminated with the virus
While hantavirus infections remain rare, proper precautions when handling rodent-infested areas are crucial. Stay informed and take necessary safety measures.

Hackman was found to have atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease along with advanced Alzheimer's disease, while his wife likely passed away first from hantavirus pulmonary syndrome. (Donaldson Collection/Michael Ochs Archives/Getty Images)
Hantavirus: Rare but Potentially Deadly Infection Linked to Rodents
Dr. Marc Siegel, clinical professor of medicine at NYU Langone Health and Fox News senior medical analyst, confirms that hantavirus can spread through dust contaminated with rodent saliva, urine, and droppings.
Which Rodents Carry Hantavirus?
The deer mouse is the most common carrier of hantavirus in the United States, Siegel noted.
Where Is Hantavirus Most Common?
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), hantavirus cases are most often reported in rural areas, where rodents have easier access to homes, barns, and storage spaces.
👉 Read More Health Articles Here
Hantavirus Symptoms and Fatality Rate
✔ Early symptoms (1–8 weeks after exposure):
- Fever
- Muscle aches
- Fatigue
- Gastrointestinal issues
✔ Severe symptoms (4–10 days later):
- Coughing
- Shortness of breath
- Fluid buildup in the lungs
Hantavirus infections are incredibly rare, both experts agree. However, one-third to one-half of cases are fatal, making early detection and medical care essential.
Dr. Rhys Parry noted, “I’m honestly impressed they were able to determine it was HPS after the fact.”
Although human-to-human transmission is not common in the U.S., experts recommend preventative measures when dealing with rodent infestations.

Hantaviruses include a group of viruses primarily carried by rodents that can cause severe respiratory or renal diseases in humans. (iStock)
Sin Nombre Virus: The Leading Cause of Hantavirus Pulmonary Syndrome in the U.S.
The Sin Nombre virus is the most common hantavirus in the United States, responsible for causing Hantavirus Pulmonary Syndrome (HPS). This condition has a 38% mortality rate, making it a serious but rare infectious disease.
How Hantavirus Becomes Fatal
Dr. Rhys Parry explains that HPS typically turns fatal when fluid fills the lungs, leading to respiratory failure and a lack of oxygen reaching vital organs.
Is There a Treatment for Hantavirus?
Currently, no specific antiviral treatment exists for hantavirus infections. However, early intensive care and oxygen therapy can help manage symptoms and improve survival rates.
✔ The CDC emphasizes the importance of early medical intervention, stating,
"Patients with sudden acute disease can rapidly become severely ill and die, making early intensive medical care critical."
While rare, hantavirus infections require urgent attention, especially in high-risk rural areas where rodent exposure is more common.
Hantaviruses can cause severe illnesses, hemorrhagic fever, renal disease or hantavirus pulmonary syndrome. (iStock)
Hantavirus Treatment & Prevention: What You Need to Know
Dr. Rhys Parry warns that once a patient experiences full respiratory distress, treatment becomes less effective, emphasizing the importance of early medical intervention.
Supportive Care for Hantavirus Patients
Since there is no specific antiviral treatment for hantavirus, doctors rely on supportive care to manage symptoms, including:
✔ Monitoring heart function
✔ Administering fluids and oxygen therapy
✔ Using a ventilator in severe cases
✔ Broad-spectrum antibiotics, fever reducers, and pain relievers
How to Prevent Hantavirus Exposure
✔ Rodent control – Keep homes, barns, and storage areas rodent-free
✔ Proper cleaning – Use protective gear when handling rodent-infested areas
✔ Avoid exposure – Stay away from areas where rodents are common
👉 Early detection and prevention are key to reducing the risk of hantavirus infection.
